The Routledge volume Researching Non-State Actors in International Security: Theory and Practice, edited by Andreas Kruck and Andrea Schneiker, has now been turned into a fully open access book. The book contains chapters on “interpreting texts” (Part I), “establishing causal claims” (Part II), and “doing fieldwork” (Part III). I contributed a chapter on “Qualitative Comparative Analysis and the Study of Non-State Actors” to Part II of the volume. The book’s substantive chapters are complemented by “discussion chapters” where commentators draw together and reflect upon the respective areas of research. Many thanks to the editors and other contributors for their efforts turning this into an open access book! I am grateful for the open access funding approved by the University of Erfurt to contribute to this aim.
Category: Publication
-
BJPIR Most Cited Article
The British Journal of Politics and International Relations (BJPIR) highlights our article “Parliaments in Security Policy: Involvement, Politicisation, and Influence” (with Dirk Peters, Peace Research Institute Frankfurt) as the most cited article in this journal in the last 3 years (as of January 7, 2021). Notably, 5 of the 10 most cited articles stem from our special issue on parliaments and security policy. Thanks to all our contributors for turning this collective project into such a success!

Abstract: While parliaments have long been neglected actors in the analysis of security policy, a research literature on the subject is growing. Current research is focused primarily on how parliaments, relying on formal legal competences, can constrain governmental policies. However, this research needs expansion in three areas. First, informal sources of parliamentary influence on security policy deserve more systematic attention as the significance of parliaments often hinges on contextual factors and individual decision-makers. Second, we still lack a systematic understanding of the effects of parliamentary involvement on security policy. Finally, the role of parliaments for the politics of security is almost completely uncharted territory. When parliaments become involved in security policy, does it foster transparency and contribute to the politicisation of security policy so that security policy becomes a ‘normal’ political issue? The article reviews current research, derives findings from the contributions to this Special Issue, and spells out their wider implications.
Introduction to the special issue:
Mello, Patrick A., and Dirk Peters (2018) ‘Parliaments in Security Policy: Involvement, Politicisation, and Influence’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117745684.
Contributing articles:
Strong, James (2018) ‘The War Powers of the British Parliament: What Has Been Established and What Remains Unclear?’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117745767.
Kaarbo, Juliet (2018) ‘Prime Minister Leadership Style and the Role of Parliament in Security Policy’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117745679.
Kriner, Douglas L. (2018) ‘Congress, Public Opinion, and an Informal Constraint on the Commander-in-Chief’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117745860.
Rosén, Guri, and Kolja Raube (2018) ‘Influence Beyond Formal Powers: The Parliamentarisation of European Union Security Policy’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117747105.
Schade, Daniel (2018) ‘Limiting or Liberating? The Influence of Parliaments on Military Deployments in Multinational Settings’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117746918.
Oktay, Sibel (2018) ‘Chamber of Opportunities: Legislative Politics and Coalition Security Policy’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117745680.
Wagner, Wolfgang (2018) ‘Is There a Parliamentary Peace? Parliamentary Veto Power and Military Interventions from Kosovo to Daesh’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117745859.
Lagassé, Philippe, and Patrick A. Mello (2018) ‘The Unintended Consequences of Parliamentary Involvement: Elite Collusion and Afghanistan Deployments in Canada and Germany’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117745681.
Raunio, Tapio (2018) ‘Parliament as an Arena for Politicization: The Finnish Eduskunta and Crisis Management Operations’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117745682.
Hegemann, Hendrik (2018) ‘Towards ‘Normal’ Politics? Security, Parliaments and the Politicisation of Intelligence Oversight in the German Bundestag’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117745683.
-
Open Access FPA Article
Our recent Foreign Policy Analysis article “Patterns of Political Ideology and Security Policy” (with Tim Haesebrouck, Ghent University) has been turned into Gold Open Access by Oxford University Press. The PDF can now be freely accessed. We thank the University of Erfurt for approving our funding application.
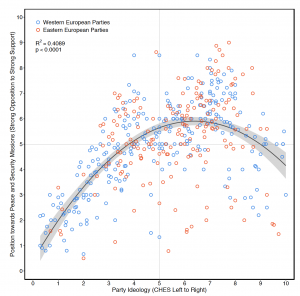
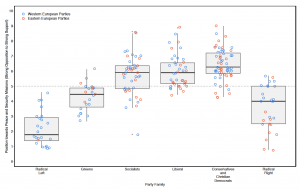
Abstract: Recent studies on political ideology suggest the existence of partisan divides on matters of foreign and security policy – challenging the notion that “politics stops at the water’s edge”. However, when taken as a whole, extant work provides decidedly mixed evidence of party-political differences outside domestic politics. This article first conducts a systematic empirical analysis of the relationship between parties’ left-right positions and their general attitude towards peace and security missions, which suggests that right-leaning parties tend to be more supportive of military operations. Yet, the results also show that the empirical pattern is curvilinear: centrist and center-right parties witness the highest level of support for military missions, while parties on both ends of the political spectrum show substantially less support. The second part of our analysis examines whether the stronger support of rightist parties for peace and security missions translates into a greater inclination of right-wing governments to actually deploy forces to military operations. Strikingly, our results suggest that leftist governments were actually more inclined to participate in operations than their right-leaning counterparts. The greater willingness of left-wing executives to deploy military forces is the result of their greater inclination to participate in operations with inclusive goals.
-
Leadership Traits and Political Beliefs in German Foreign Policy
Book review published in German Politics
On December 21, 2020, German Politics (Taylor & Francis) published my book review of Entscheidungsträger in der deutschen Außenpolitik: Führungseigenschaften und politische Überzeugungen der Bundeskanzler und Außenminister (Nomos) by Christian Rabini, Katharina Dimmroth, Klaus Brummer, and Mischa Hansel.
From the review: “In sum, this book offers a compelling account of German leaders and their foreign policies, based on meticulous research and a systematic application of leadership profiling. The book’s methods should stimulate wide application in the field of foreign policy analysis, and beyond.”
-
Patterns of Political Ideology and Security Policy
The October 2020 issue of Foreign Policy Analysis (Oxford University Press) includes the article “Patterns of Political Ideology and Security Policy” by Tim Haesebrouck and me. In the article, we examine the relationship between the ideology of political parties and their general support for military missions. Empirically, the study confirms a curvilinear relationship: with support peaking among center-right parties and dropping the further one moves to the far-left and far-right. However, when looking at actual military participation the pattern is different. Here, left-of-center parties have deployed to military missions more often than their rightist counterparts. Founded in 2005, Foreign Policy Analysis (FPA) aims to serve “as a source for efforts at theoretical and methodological integration and deepening the conceptual debates throughout this rich and complex research tradition”. The journal is published by Oxford University Press under the auspices of the International Studies Association (ISA).
Abstract: Recent studies on political ideology suggest the existence of partisan divides on matters of foreign and security policy – challenging the notion that “politics stops at the water’s edge”. However, when taken as a whole, extant work provides decidedly mixed evidence of party-political differences outside domestic politics. This article first conducts a systematic empirical analysis of the relationship between parties’ left-right positions and their general attitude towards peace and security missions, which suggests that right-leaning parties tend to be more supportive of military operations. Yet, the results also show that the empirical pattern is curvilinear: centrist and center-right parties witness the highest level of support for military missions, while parties on both ends of the political spectrum show substantially less support. The second part of our analysis examines whether the stronger support of rightist parties for peace and security missions translates into a greater inclination of right-wing governments to actually deploy forces to military operations. Strikingly, our results suggest that leftist governments were actually more inclined to participate in operations than their right-leaning counterparts. The greater willingness of left-wing executives to deploy military forces is the result of their greater inclination to participate in operations with inclusive goals.
-
Democracies and Withdrawal from Iraq
Open Access Article Published in EJIS
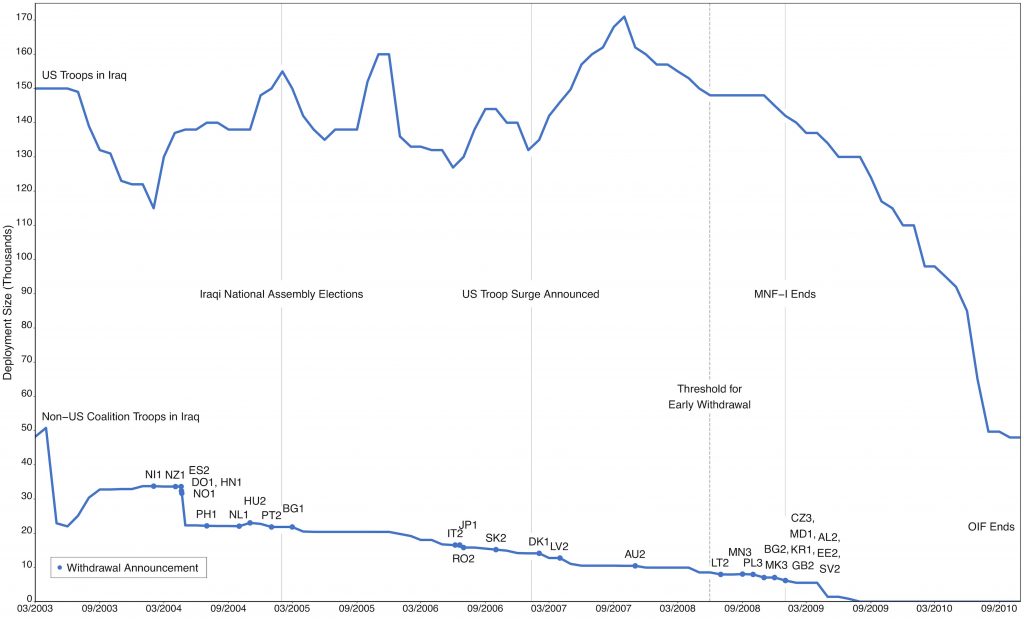
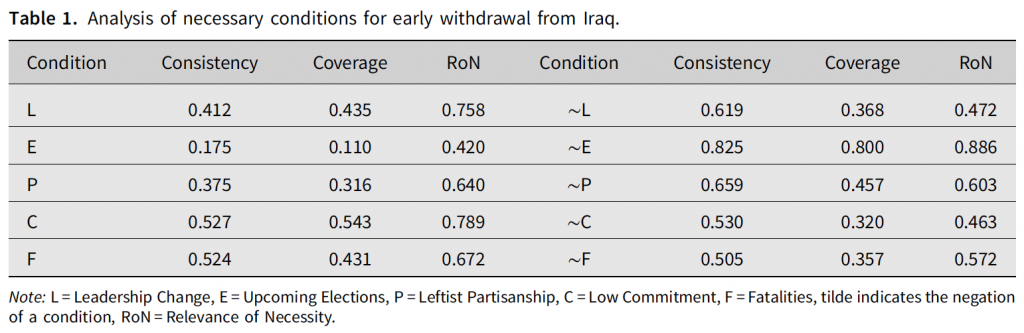
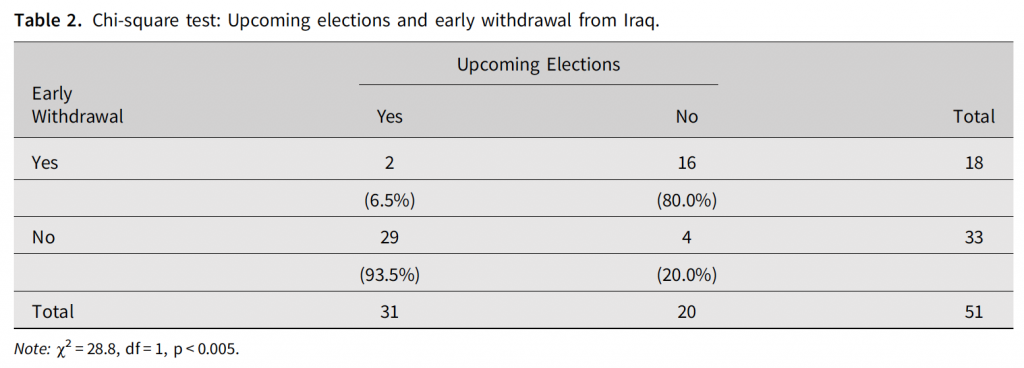
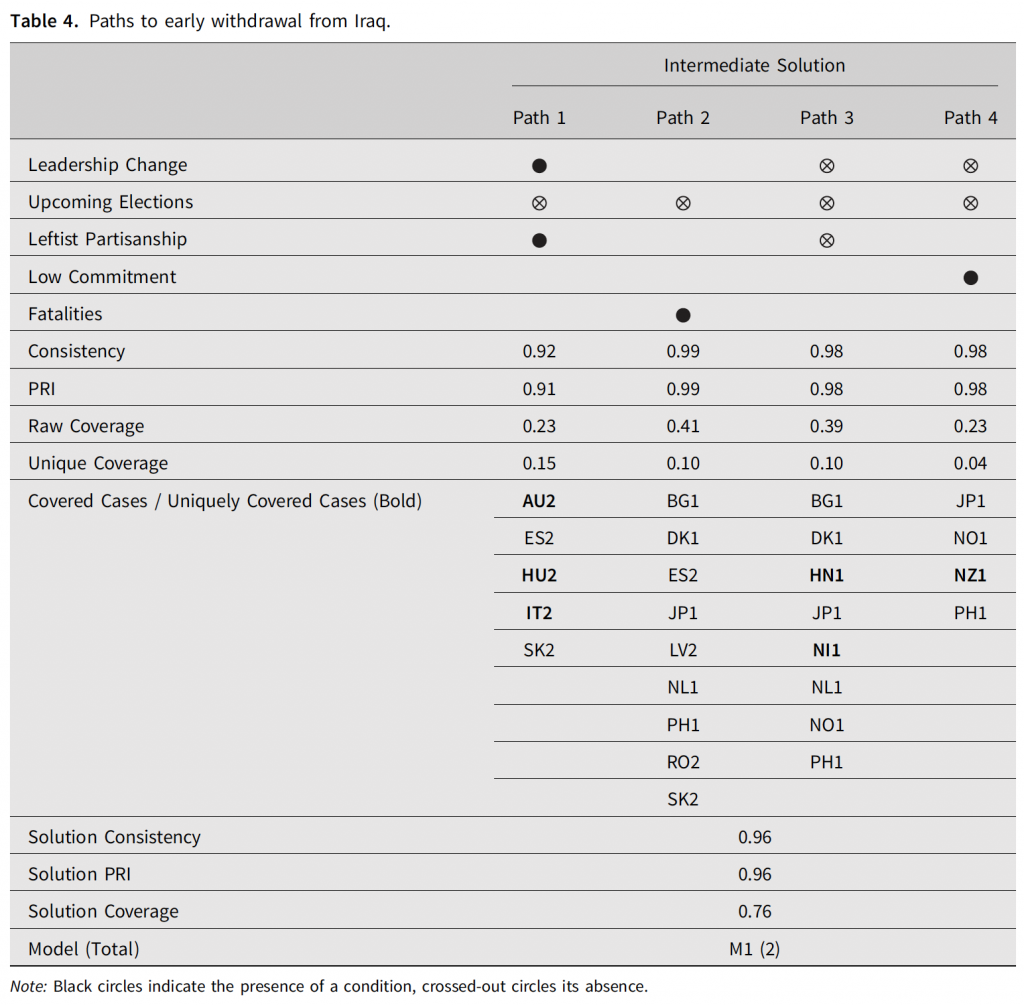
The February 2020 issue (5:1) of the European Journal of International Security (Cambridge University Press) features the article “Paths towards Coalition Defection: Democracies and Withdrawal from the Iraq War“. The study examines democratic war involvement in Iraq across 51 leaders from 29 countries. The article is the first QCA study that covers the entire period of coalition operations in Iraq, from 2003 until 2010, across all democratic governments that were involved in the multinational coalition. Among other findings, the article challenges some previous studies’ results on the effects of leadership turnover and electoral incentives (here and here). The set-theoretic analysis documents causal heterogeneity, where multiple paths lead towards coalition defection and leadership turnover only brought about the outcome of coalition withdrawal when combined with specific other conditions. For electoral incentives, contrary to expectations derived from prior studies, it could not be shown that upcoming elections were associated with coalition defection. Finally, the article documents the importance of casualties and prior commitment as factors that had previously been neglected. Replication data is hosted a Harvard Dataverse (R script, data, supplement).
Abstract: Despite widespread public opposition to the Iraq War, numerous democracies joined the US-led multinational force. However, while some stayed until the end of coalition operations, and several increased their deployments over time, others left unilaterally. How to explain this variation?
While some studies suggest that democratic defection from security commitments is primarily motivated by electoral incentives or leadership change, scholars have not reached a consensus on this issue. To account for the complex interplay between causal factors, this article develops an integrative theoretical framework, using fuzzy-set Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA) on original data on the Iraq War involvement of 51 leaders from 29 democracies.
The findings document the existence of multiple paths towards coalition defection. Among others, the results show that: (1) leadership change led to early withdrawal only when combined with leftist partisanship and the absence of upcoming elections; (2) casualties and coalition commitment played a larger role than previously assumed; and (3) coalition defection often occurred under the same leaders who had made the initial decision to deploy to Iraq, and who did not face elections when they made their withdrawal announcements.
Reference:
Mello, Patrick A. (2020) Paths towards Coalition Defection: Democracies and Withdrawal from the Iraq War, European Journal of International Security 5 (1): 45-76 (https://doi.org/10.1017/eis.2019.10)
-
Von der Bonner zur Berliner Republik
Sammelband der DVPW-Themengruppe Außen- und Sicherheitspolitik
In der bei Nomos erscheinenden Buchreihe “Außenpolitik und Internationale Ordnung” (Herausgeber: Hanns W. Maull und Sebastian Harnisch) ist der von Klaus Brummer und Friedrich Kießling herausgegebene Sammelband Zivilmacht Bundesrepublik? Bundesdeutsche außenpolitische Rollen vor und nach 1989 aus politik- und geschichtswissenschaftlichen Perspektiven erschienen.
Die Publikation ist der dritte bisher erschienene Sammelband in der “Edition Themengruppe Außen- und Sicherheitspolitik“. Weitere Bände sind Chinesische Seidenstraßeninitiative und amerikanische Gewichtsverlagerung (Hansel/Harnisch/Godehardt, Hrsg. 2018) sowie Sonderbeziehungen als Nexus zwischen Außenpolitik und internationalen Beziehungen (Harnisch/Brummer/Oppermann, Hrsg. 2015).
Weiterführende Informationen zur Themengruppe Außen- und Sicherheitspolitik gibt es auf der DVPW-Webseite. Dort ist auch die Anmeldung zur Mailingliste der Themengruppe möglich. Der Twitter-Account ist @dvpw_aussenpol.
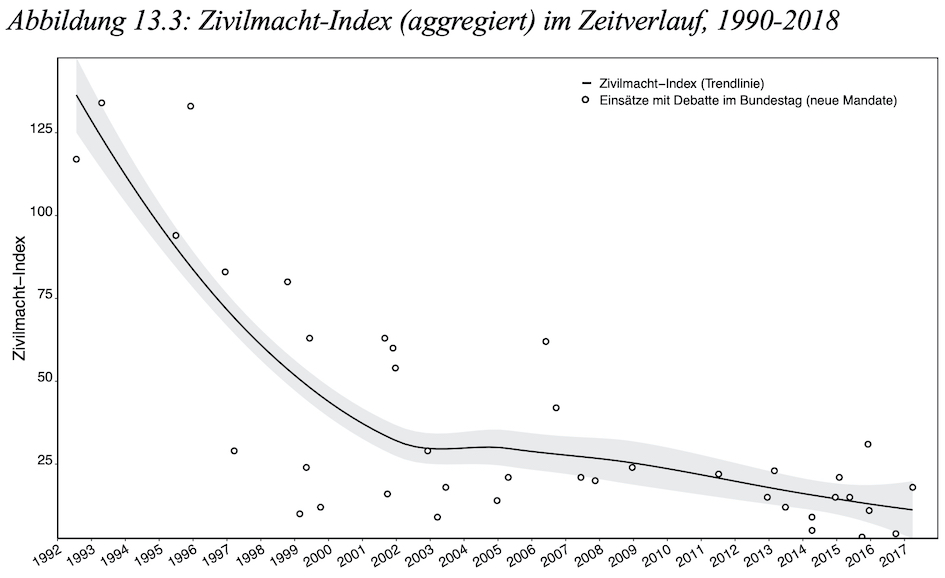
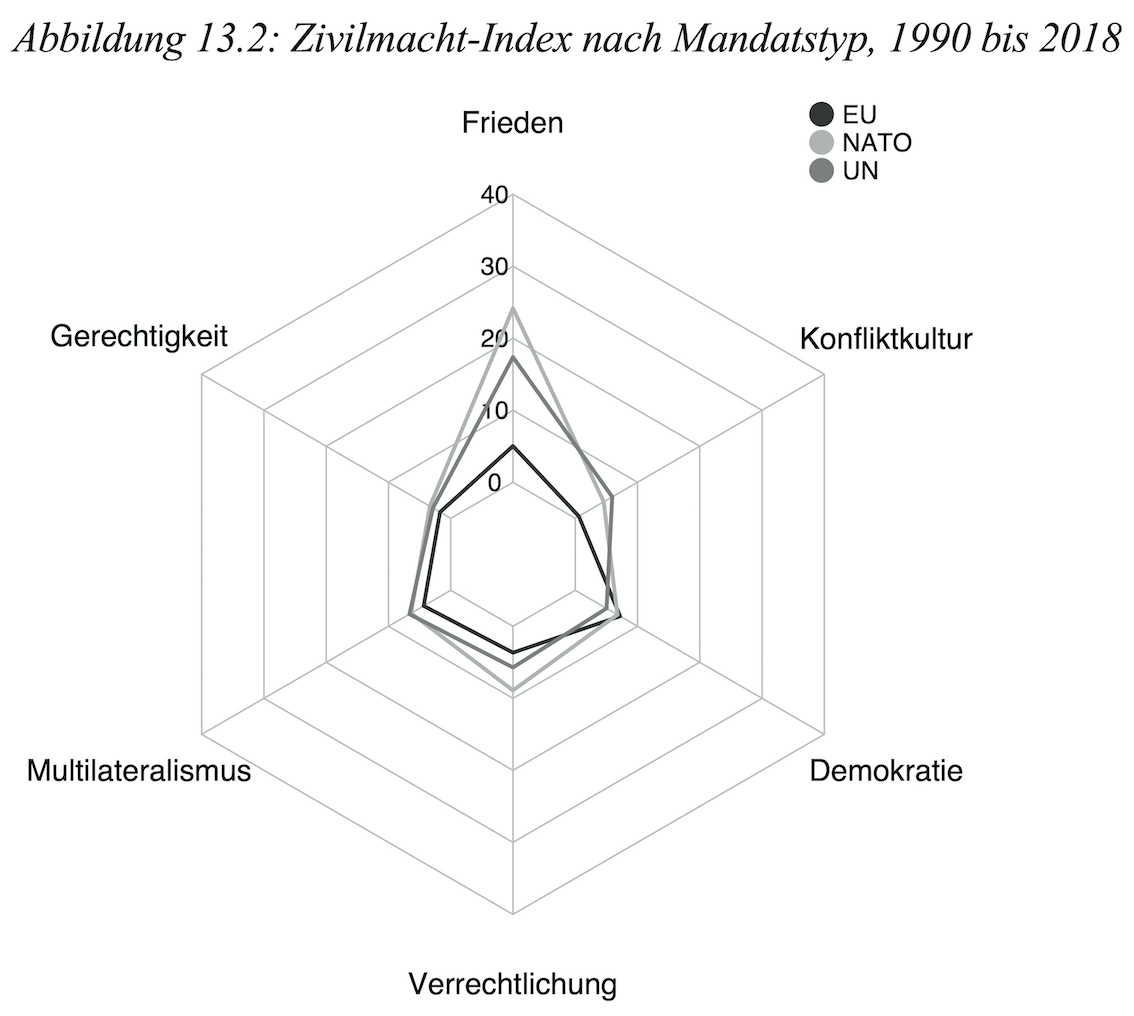
Mein Kapitel “Von der Bonner zur Berliner Republik” (PDF) untersucht für den Zeitraum 1990 bis 2018 parlamentarische Debatten zu 40 Auslandseinsätzen der Bundeswehr im Hinblick auf deren Resonanz mit dem rollentheoretischen Konzept der “Zivilmacht”. Die quantitative Textanalyse zeigt im Zeitverlauf eine deutliche Abnahme der Verwendung zivilmachtstheoretischer Rhetorik:
“Während die Debatten Anfang der 1990er Jahre noch von einer hohen Resonanz mit dem Zivilmachtkonzept geprägt waren, so zeigt sich seither eine kontinuierliche Abnahme. Dies kann als Anzeichen für einen „Wandel“ in der deutschen Außenpolitik und ihrer politischen Rechtfertigung gesehen werden. Zweitens konnte die Analyse Unterschiede zwischen den Einsatztypen identifizieren. So zeigen die Plenardebatten zu NATO-Einsätzen eine höhere Übereinstimmung mit dem Zivilmachtkonzept auf als UN- oder EU-Missionen. Statistisch signifikant sind dabei die Zivilmacht-Werte der Debatten zu EU-Einsätzen, welche im Vergleich zur Gesamtheit der untersuchten Plenardebatten erheblich niedriger liegen” (Mello 2019: 310).
-
Paths towards Coalition Defection
Article Published in the European Journal of International Security
The European Journal of International Security (Cambridge University Press) has published a first view version of “Paths towards Coalition Defection: Democracies and Withdrawal from the Iraq War“. The open access article PDF is available here. Replication data is hosted a Harvard Dataverse (R script, data, supplement). The article examines democratic war involvement in Iraq across 51 leaders from 29 democracies. It is the first set-theoretic study that covers the entire time frame of coalition operations, from 2003 until 2010. Its counter-intuitive findings document the existence of multiple paths towards coalition defection, emphasizing the importance of casualties and prior commitment. The European Journal of International Security (EJIS), founded in 2016, aims to publish “the cutting-edge of security research”, taking a cross-disciplinary approach that seeks to cover all areas of international and global security. EJIS is a journal of the British International Studies Association (BISA).
Abstract: Despite widespread public opposition to the Iraq War, numerous democracies joined the US-led multinational force. However, while some stayed until the end of coalition operations, and several increased their deployments over time, others left unilaterally. How to explain this variation? While some studies suggest that democratic defection from security commitments is primarily motivated by electoral incentives or leadership change, scholars have not reached a consensus on this issue. To account for the complex interplay between causal factors, this article develops an integrative theoretical framework, using fuzzy-set Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA) on original data on the Iraq War involvement of 51 leaders from 29 democracies. The findings document the existence of multiple paths towards coalition defection. Among others, the results show that: (1) leadership change led to early withdrawal only when combined with leftist partisanship and the absence of upcoming elections; (2) casualties and coalition commitment played a larger role than previously assumed; and (3) coalition defection often occurred under the same leaders who had made the initial decision to deploy to Iraq, and who did not face elections when they made their withdrawal announcements.
-
The Politics of Multinational Military Operations
Special Forum, Contemporary Security Policy
Contemporary Security Policy (CSP) has published a Special Forum on “The Politics of Multinational Military Operations”, guest edited by Patrick A. Mello (University of Erfurt) and Stephen M. Saideman (Carleton University). The special forum contains contributions from Gunnar Fermann (Norwegian University of Science and Technology), Per Marius Frost-Nielsen (Norwegian University of Science and Technology), Olivier Schmitt (University of Southern Denmark), Daan Fonck (Katholieke Universiteit Leuven), Tim Haesebrouck (Ghent University), Yf Reykers (Katholieke Universiteit Leuven), Stéfanie von Hlatky (Queen’s University), Justin Massie (Université du Québec à Montréal), and Kathleen J. McInnis (Congressional Research Service). CSP is a peer reviewed journal published by Taylor & Francis. The journal is indexed in the Social Science Citation Index, expecting its first Impact Factor for June/July 2019 (International Relations). CSP has a Scopus CiteScore of 1.07 (2017) and is ranked in the first quartile in Political Science & International Relations [more information].
Introduction to the Special Forum:
Mello, Patrick A., and Stephen M. Saideman (2019) The Politics of Multinational Military Operations, Contemporary Security Policy 40 (1), https://doi.org/10.1080/13523260.2018.1522737 (Open Access)
Contributing Articles (in alphabetical order):
Fermann, Gunnar and Per Marius Frost-Nielsen (2019) Conceptualizing Caveats for Political Research, Contemporary Security Policy 40(1), https://doi.org/10.1080/13523260.2018.1523976
Fonck, Daan, Tim Haesebrouck and Yf Reykers (2019) Parliamentary Involvement, Party Ideology and Majority-Opposition Bargaining: Belgian Participation in Multinational Military Operations, Contemporary Security Policy 40(1), https://doi.org/10.1080/13523260.2018.1500819
Mcinnis, Kathleen J. (2019) Varieties of Defection Strategies from Multinational Military Operations: Insights from Operation Iraqi Freedom, Contemporary Security Policy 40(1), https://doi.org/10.1080/13523260.2018.1506964
Mello, Patrick A. (2019) National Restrictions in Multinational Military Operations: A Conceptual Framework, Contemporary Security Policy 40(1), https://doi.org/10.1080/13523260.2018.1503438 (Open Access)
Schmitt, Olivier (2019) More Allies, Weaker Missions? How Junior Partners Contribute to Multinational Military Operations, Contemporary Security Policy 40(1), https://doi.org/10.1080/13523260.2018.1501999
Von Hlatky, Stéfanie and Justin Massie (2019) Ideology, Ballots, and Alliance: Canadian Participation in Multinational Military Operations, Contemporary Security Policy 40(1), https://doi.org/10.1080/13523260.2018.1508265
-
Privatisierung in der Sicherheitspolitik
Perspektiven der Forschung zur Privatisierung in der Sicherheitspolitik
In der aktuellen Ausgabe der Zeitschrift für Friedens- und Konfliktforschung (ZeFKo, 7. Jahrgang, 1. Heft) ist ein Beitrag von mir erschienen. Die Replik “Perspektiven der Forschung zur Privatisierung in der Sicherheitspolitik” auf den im selben Heft enthaltenen Artikel von Andreas Kruck “Wann und wie ist die Privatisierung von Sicherheit umkehrbar?” ist Teil eines Sonderhefts zu “Privatisierung von Sicherheit in Deutschland” der Gastherausgeberinnen Andrea Schneiker und Jutta Joachim, mit weiteren Beiträgen von Nathalie Hirschmann, Thomas Schmidt-Lux und Eva Herschinger. Das ZeFKO-Themenheft kann hier über die NOMOS eLibrary eingesehen werden (die Einleitung ist frei zugänglich, ein Preprint meines Beitrags kann hier heruntergeladen werden).