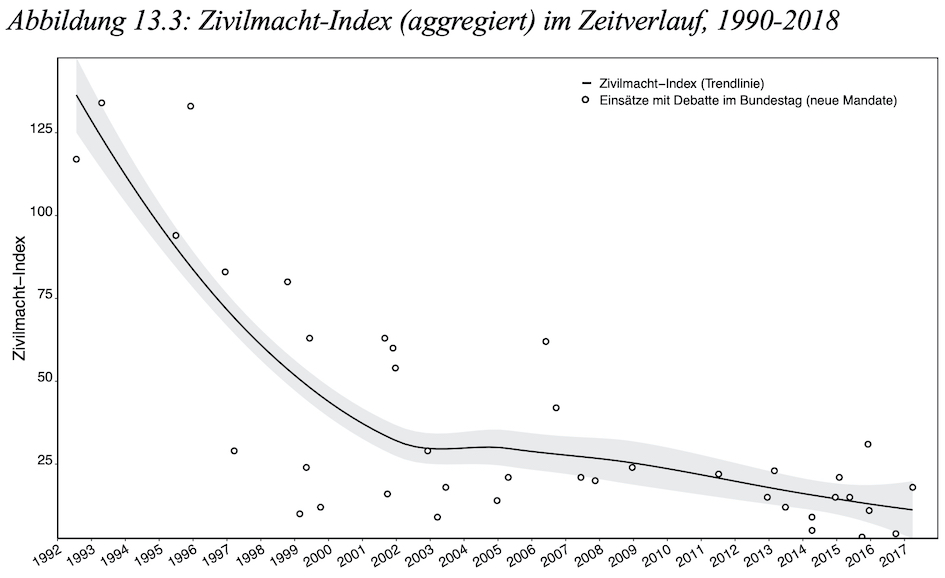
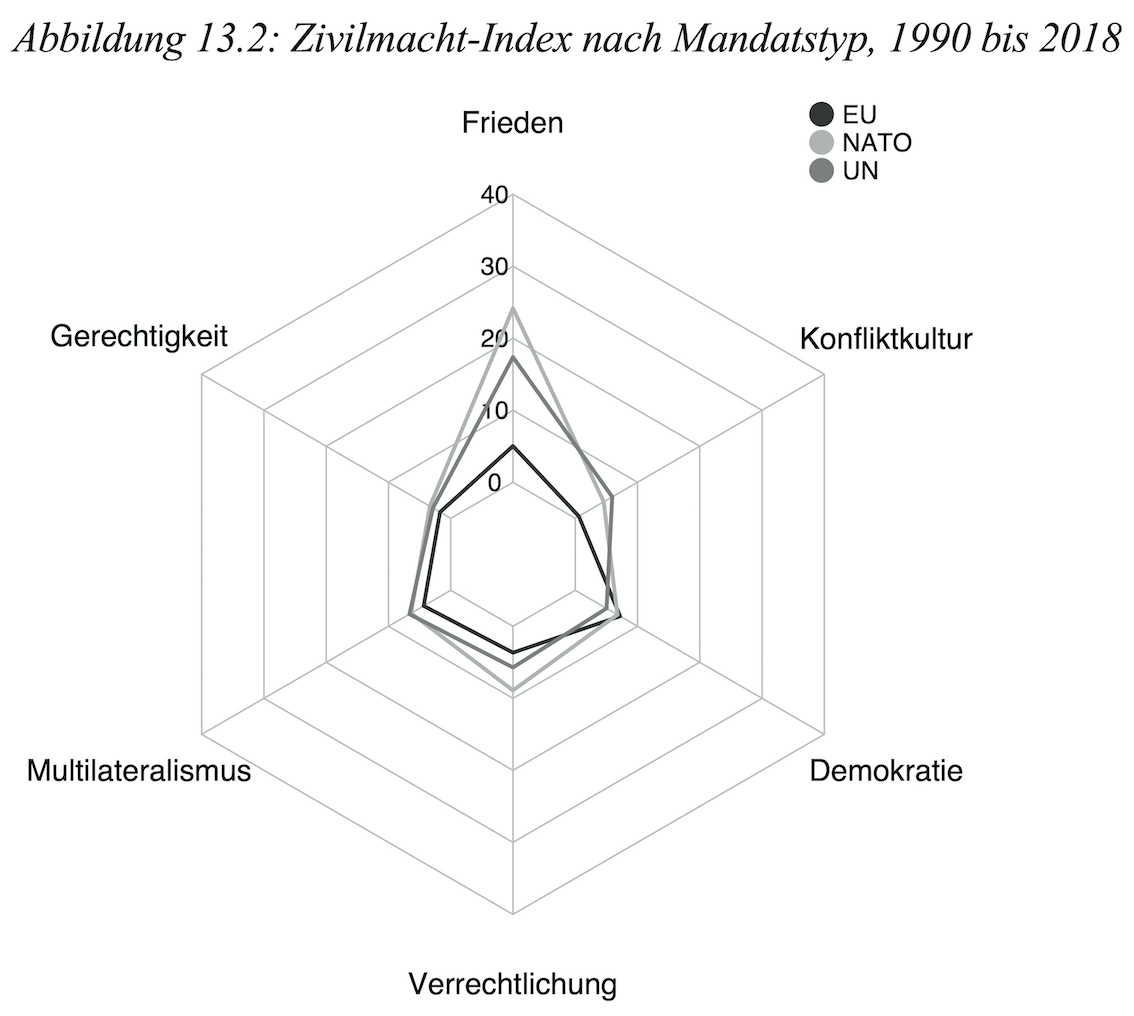
BJPIR Special Issue – Parliaments in Security Policy: Involvement, Politicisation, and Influence
The British Journal of Politics and International Relations (BJPIR) has published a Special Issue, guest edited by Patrick A. Mello and Dirk Peters: “Parliaments in Security Policy: Involvement, Politicisation, and Influence”. The special issue focuses on the pivotal democratic institution – parliament – to study legislative involvement in security matters and its effects on policy outcomes. The contributing articles employ a diverse set of theoretical perspectives and methods to explore the role of 11 different parliamentary bodies from a broad range of contemporary Western democracies. BJPIR is a peer reviewed journal of the Political Studies Association of the UK with an Impact Factor of 1.423 (2016) and Rankings of 62/165 in Political Science and 24/86 in International Relations [More Information].
Abstract: “While parliaments have long been neglected actors in the analysis of security policy, a research literature on the subject is growing. Current research is focused primarily on how parliaments, relying on formal legal competences, can constrain governmental policies. However, this research needs expansion in three areas. First, informal sources of parliamentary influence on security policy deserve more systematic attention as the significance of parliaments often hinges on contextual factors and individual decision-makers. Second, we still lack a systematic understanding of the effects of parliamentary involvement on security policy. Finally, the role of parliaments for the politics of security is almost completely uncharted territory. When parliaments become involved in security policy, does it foster transparency and contribute to the politicisation of security policy so that security policy becomes a ‘normal’ political issue? The article reviews current research, derives findings from the contributions to this Special Issue, and spells out their wider implications.” [Read Further]
Introduction to the Special Issue:
Mello, Patrick A., and Dirk Peters (2018) ‘Parliaments in Security Policy: Involvement, Politicisation, and Influence’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117745684.
Contributing Articles (in alphabetical order):
Hegemann, Hendrik (2018) ‘Towards ‘Normal’ Politics? Security, Parliaments and the Politicisation of Intelligence Oversight in the German Bundestag’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117745683.
Kaarbo, Juliet (2018) ‘Prime Minister Leadership Style and the Role of Parliament in Security Policy’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117745679.
Kriner, Douglas L. (2018) ‘Congress, Public Opinion, and an Informal Constraint on the Commander-in-Chief’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117745860.
Lagassé, Philippe, and Patrick A. Mello (2018) ‘The Unintended Consequences of Parliamentary Involvement: Elite Collusion and Afghanistan Deployments in Canada and Germany’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117745681.
Oktay, Sibel (2018) ‘Chamber of Opportunities: Legislative Politics and Coalition Security Policy’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117745680.
Raunio, Tapio (2018) ‘Parliament as an Arena for Politicization: The Finnish Eduskunta and Crisis Management Operations’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117745682.
Rosén, Guri, and Kolja Raube (2018) ‘Influence Beyond Formal Powers: The Parliamentarisation of European Union Security Policy’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117747105.
Schade, Daniel (2018) ‘Limiting or Liberating? The Influence of Parliaments on Military Deployments in Multinational Settings’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117746918.
Strong, James (2018) ‘The War Powers of the British Parliament: What Has Been Established and What Remains Unclear?’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117745767.
Wagner, Wolfgang (2018) ‘Is There a Parliamentary Peace? Parliamentary Veto Power and Military Interventions from Kosovo to Daesh’, British Journal of Politics and International Relations https://doi.org/10.1177/1369148117745859.